Local Topographic Reference
Detailed topographic base of urban areas
The Local Topographic Reference (RTL) is the topographic reference base with full coverage or of municipal management areas or geographic areas of specific themes that require detailed topographic information.
It includes information related to the following layers: relief, hydrography, road network and other transport networks; buildings, constructions and facilities; land cover, toponymy and municipal inventories.
This is an evolution of the 1:1,000 topographic cartography that was produced until now (also called urban cartography in some cases): it was born with purely cartographic characteristics and the RTL expands its possibility of exploitation in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and in 3D environments, among others.
Technical characteristics
- The precision of this data set is equivalent to 1:1,000 topographic cartography.
- This geoinformation is distributed in Geopackage 2D and 3D formats, Geodatabase, DWG 2D and 3D (both also with object data), DGN 2D and 3D, and IFC for BIM. It can also be used through the associated WMS, for visualization in applications compatible with this protocol.
- The coordinate system used is the official one in Catalonia (ETRS89 UTM 31 North) and the altitudes refer to the mean sea level in Alicante.
For the correct visualization of the data with the predefined style and for other considerations, we suggest that you consult the manuals included as annexes in the technical specifications of this geoinformation.
| Geoinformation from the Cartographic and Geological Institute of Catalonia, and also from the Girona Provincial Council and the Tarragona Provincial Council in the municipalities of the corresponding demarcations, subject to a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license (CC BY 4.0) More information |
Description
It is the detailed topographic base, equivalent to a scale of 1:1,000, mainly of the urban areas of Catalonia, developed as a spatial database and distributed in CAD, GIS and BIM formats to facilitate its exploitation in various areas.
This data set contains many elements, all of which are described in its technical specifications, and can be obtained through various mechanisms, sources and technologies. It should be noted that, in addition to the data capture, there is a task of assigning values to each of the defined attributes, in addition to the corresponding quality controls.
Given the novelty of the RTL data model, approximately 230 municipalities are initially published, to which the rest of Catalonia will be added progressively (mainly urban areas).
The final result is a data set with the following layers:
- Relief: This layer groups together the objects that allow the relief to be characterized, such as contour lines, elevations, terrace edges and slopes.
- Hydrography: This layer includes objects that allow the complete, continuous and connected linear hydrographic network to be defined, as well as natural and artificial water bodies and access points to the water network or groundwater. Some of these elements are river courses, floodplains, canals, ponds and wells.
- Land covers: This layer includes a small number of natural and artificial covers, and vegetation objects.
- Transport: The layer includes communication routes for vehicles or people as well as associated infrastructure. The objects allow the complete, continuous and connected linear road and rail networks to be defined. Air navigation routes and waterways are not included.
- Signage: This layer includes objects for the organization of urban mobility, basically vertical signs and horizontal signage.
- Constructions: This layer includes buildings and constructions that are not in other layers. It also includes enclosures, public or private, intended for uses, facilities or services with an impact on the activity of the population.
- Energy and services: This layer includes objects that are part of the energy, fuel and telecommunications supply networks, such as cabinets, pipes, streetlights and solar panels.
- Furniture: This layer includes objects of the equipment installed on the public road, such as bicycle racks, benches, mailboxes, showers (on beaches...), litter bins, etc.
- Geographic names: The texts that name or characterize the objects can be attributes of the objects themselves or texts that name objects not represented in the data set.
- Terrain modeling: This layer, which is only distributed in the Geopackage 3D, DWG 3D and DGN 3D formats, includes lines to facilitate the obtaining of terrain elevation models (slope change lines, etc.).
This organization of information facilitates agile and versatile use of the data, since it allows working with all the information at once or making selections by information layers or by territorial areas, as well as changes in symbolization.
In order to guarantee the most widespread use possible, specific formats are distributed for both users who work with GIS and users who work with CAD.
The most relevant GIS formats are the Geopackage, exploitable from free software, as well as the Geodatabase, for users of the ESRI platform. In both cases, the file contains vector data organized in the different thematic layers, as well as metadata tables and descriptions of the attribute values. The files incorporate a stylization for the free software QGIS in the case of the Geopackage and for ArcGIS Pro in the case of the Geodatabase.
For users who work with CAD software, they are distributed in DGN (for MicroStation) and DWG (for AutoCAD) formats, both in 2D and with the information in 3D. In all cases, the information is grouped by levels with descriptive names and with a symbolization adapted to the destination software, as well as the attributes of the different objects incorporated into the file. In the case of the DGN format, the attributes are incorporated as itemtypes, and in the case of the DWG format they are distributed in two versions: one with attributes as tags, consultable from AutoCAD, and another with the attributes as object data, consultable from AutoCAD Map.
Additionally, the IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) format allows the incorporation of Local Topographic Reference information into BIM (Building Information Modeling) work environments. This format facilitates the integration of topographic data into architecture, engineering and construction projects, promoting interoperability between different platforms and improving project coordination.
Case studies
The main objective of this geoinformation is municipal management, as it provides a precise topographic base that serves as a reference for the development of any activity that has a territorial impact at the municipal level, including technical, management, planning or territorial administration activities.
Some examples of this municipal management would be carrying out inspection work related to various elements of public space (restaurant terraces, etc.), attending to applications for public road occupancy licenses and for the management of terraces and activities on public roads in general, generating sketches of traffic accident reports and other incidents that occur on public roads, collecting waste and carrying out related studies (location of collection points, optimal determination of routes, etc.), or drafting accessibility plans that allow defining and prioritizing actions on public roads in order to promote accessibility at the municipal level.
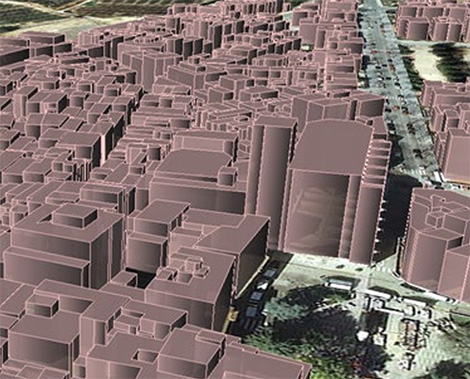
Another interesting application of RTL is the obtaining of city models, which facilitate the carrying out of studies of pollution and noise protection, solar potential, risks and civil protection, visual impact and shadows, tourism promotion, heritage protection, urban and architectural planning, and planning of communications networks, among others.
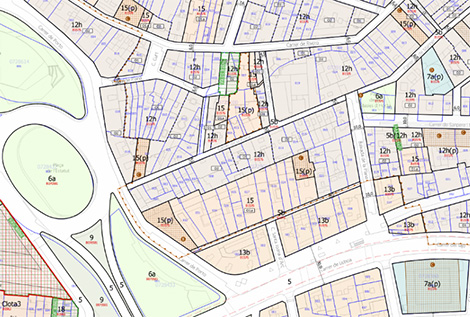
Also as was the case with the previous 1:1,000 topographic cartography, the RTL facilitates urban planning and, in any case, can serve as a general reference cartography.