LIDAR Sensor: High Precision Applicability
LIDAR data allows mapping of discrete changes at very high resolution, covering large areas uniformly and very precisely
LiDAR systems, as an operational technology at the ICGC, have several advantages. First of all, it is a system that offers high precision, high density of points, large coverage areas and the ability to fuse this data in a complementary way to that of thematic sensors, under the competences and assets of the ICGC. This entails the ability to map, reactively if necessary, discrete changes at a very high resolution, covering large areas uniformly and very precisely.
The main uses of a new LiDAR system, taking into account the competences and assets of the ICGC, as well as in particular the characteristics of our territory, include the generation of digital terrain and surface models (DSM and DTM), maps of biophysical variables of forest masses, volumetric changes in extractive activities, studies of the coastline and the hydrographic network, three-dimensional urban planning models or building models, among others.
Forestry applications based on LiDAR techniques can be considered one of the most important since it is the only sensor that is affected by multiple reflections, frequently with a range up to the ground surface. The acquisition of LiDAR data allows obtaining precious information from both the terrain and the canopy and therefore the possibility of generating metrics.
The shrub cover of the forests of Catalonia is today a very poorly determined variable, the successive National Forest Inventories (IFN2, IFN3) have never considered it and it is not expected that it will be considered in IFN4. This cover is often responsible for the rapid proliferation of fire and the lack of knowledge of it makes it difficult to carry out good forest management, to fight against large forest fires or to know the impacts of climate change on the decay of forests or the loss of biodiversity.
We currently have maps of biophysical variables of the trees estimated with data from the LiDARCAT1 project. Due to the fact that the field inventories used date from 2000 and 2001, these maps have been represented as of 2005. The new Map of Biophysical Variables of the Trees of Catalonia has recently been published in collaboration with the Center for Ecological Research and Forestry Applications with LIDARCAT 2 data and the National Forest Inventory (IFN4).
Forest products from LIDAR data

Since 2021, the ICGC has identified and delimited forest covers based on the segmentation of the tree mass in plant and height with data from the new LiDAR TM2 system, TERRAIN Mapper 2.
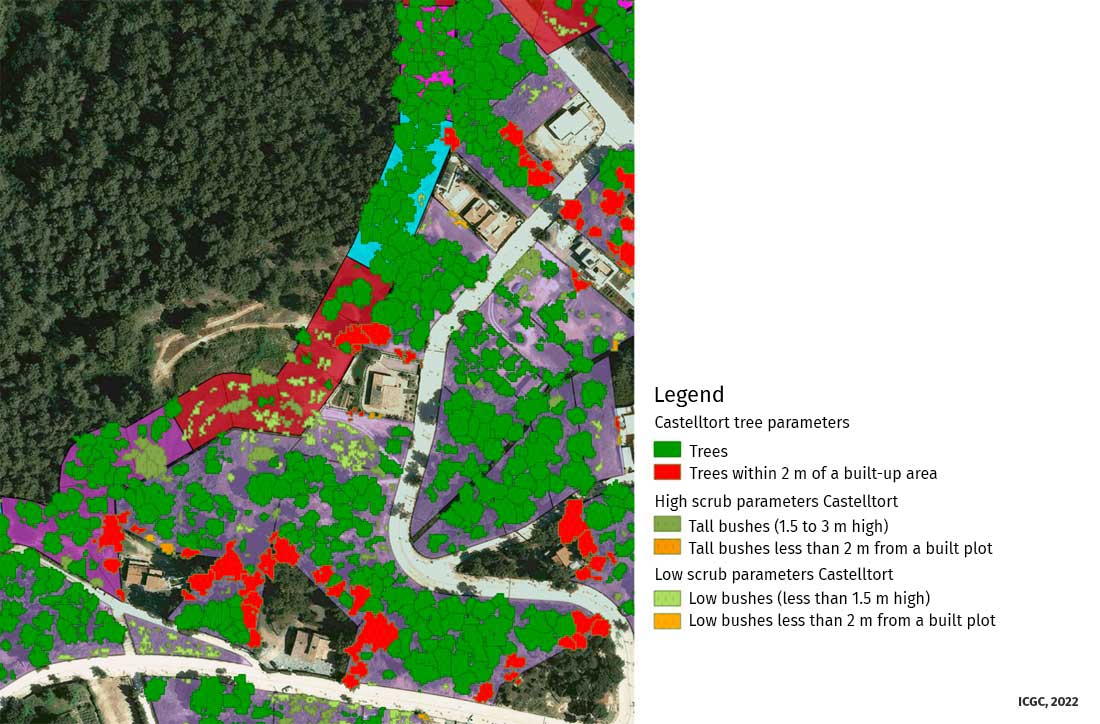
Delimitation and identification of forest covers in urbanized areas.