Coastal Lidar
Lidar point cloud coverage of the coast of Catalonia
The ICGC with Coastal LiDAR makes available the LiDAR point clouds from the periodic flights it carries out over the Catalan coast. These flights have been carried out since 2008, covering approximately 500 meters from the coastline. Initially, there was an annual campaign, but since 2021 two have been carried out: one in autumn and another in winter, and specific flights are also carried out after storms to capture significant changes.
The data is obtained with LiDAR and photographic aerial sensors, simultaneously generating an orthoimage with a resolution of 10-15 cm. The point cloud, georeferenced and with an average density of 15 points/m² (in coverages from 2021), describes the terrain morphology with great precision, while the orthoimage facilitates its interpretation. Points are classified to identify features such as terrain, vegetation, or buildings, allowing detailed information to be obtained and elevation models to be generated.
Publication date: December 2025.
Information date: 2014, 2015, 2022, 2023 and 2024.
Version: v1.0.
| Cartography subject to a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license More information |
Description
A LiDAR point cloud is a massive set of three-dimensional points obtained using laser technology (Light Detection and Ranging). Each point represents an X, Y and Z coordinate of the terrain or of the objects on it, such as vegetation, buildings or infrastructures. This information allows the reconstruction of the earth's surface and the elements that make it up in great detail, being a fundamental basis for topographic, environmental and engineering studies.
The flights are carried out with aircraft equipped with LiDAR sensors and cameras. The sensor emits laser pulses towards the terrain and measures the time it takes for each pulse to return, thus calculating the distance with great precision. Each flight covers the coastal strip (about 500 meters from the coastline) and is planned to guarantee an average density of 15 points/m². In historical coverages the average density is 1 point/m². The combination with photographic images allows the generation of simultaneous orthoimages that complement the geometric information with visual context.
The main product is the georeferenced LiDAR point cloud, which is processed to correct errors, adjust coordinates and ensure spatial coherence. Once validated, an advanced classification is applied using automatic algorithms that assign each point a category: terrain, vegetation (low, medium and high), buildings, bridges and other elements. This classification allows the generation of elevation models (MDT, MDS, MDTe), calculating volumes, analysing vegetation cover and studying coastal dynamics with great precision.
Technical characteristics
- Product: Cloud of classified LiDAR points.
- Coverage: Coastal strip of Catalonia up to 500 m from the coastline.
- Data source: Cloud of LiDAR points captured in periodic flights over the coast of Catalonia.
- Average density: 15 points/m2 in coverages from 2021 and 1 point/m2 in historical coverages.
- Classification: Advanced, main classes: terrain, vegetation, buildings, bridges, water.
- Sheet size: 1 x 1 km blocks in coverages from 2021, 2 x 2 km blocks in historical coverages.
- Reference system: EPSG: 25831.
- Format: LAZ 1.4 with color and RGBI infrared, historical flights without color.
- Update: Twice a year (winter and autumn) more specific for coastal storms, more historical data.
Use cases
Elevation models
LiDAR point clouds from coastal flights allow the generation of high-precision elevation models, such as the Digital Terrain Model (DTM), the Digital Surface Model (DSM) and the Digital Terrain Model with Buildings (DTBM). These models are essential for analyzing coastal dynamics, identifying changes in the coastline and studying the impact of storms on beaches and dune systems. They are also a fundamental basis for flood risk studies, as they provide detailed information on the relief and elevations, allowing the simulation of risk scenarios and the planning of protection measures. The density of 15 points/m² guarantees an accurate representation of both the natural relief and the infrastructures near the coast.
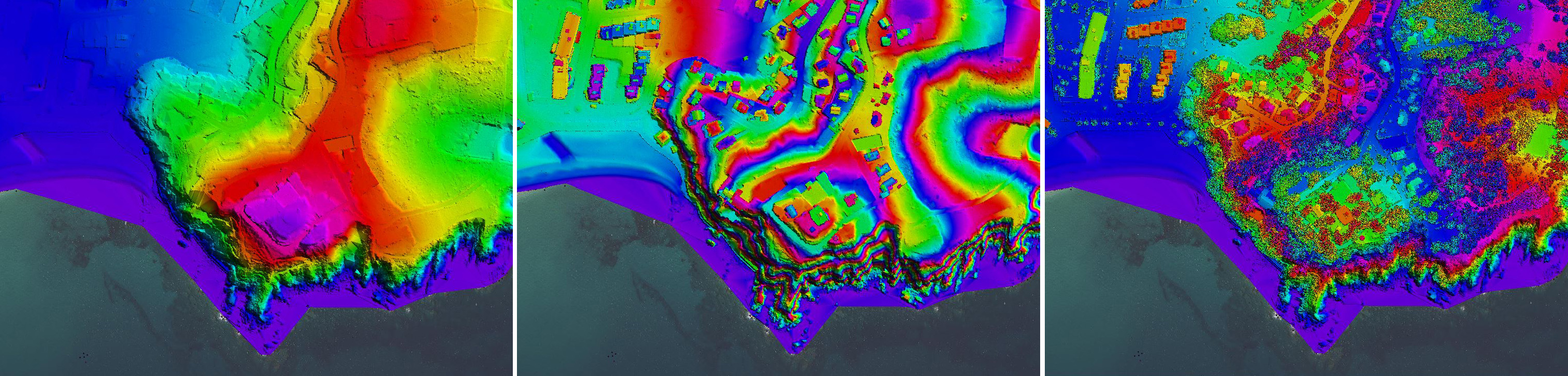
Winter Coast 2022 Fenals (Lloret de Mar, Selva)
Vegetation study
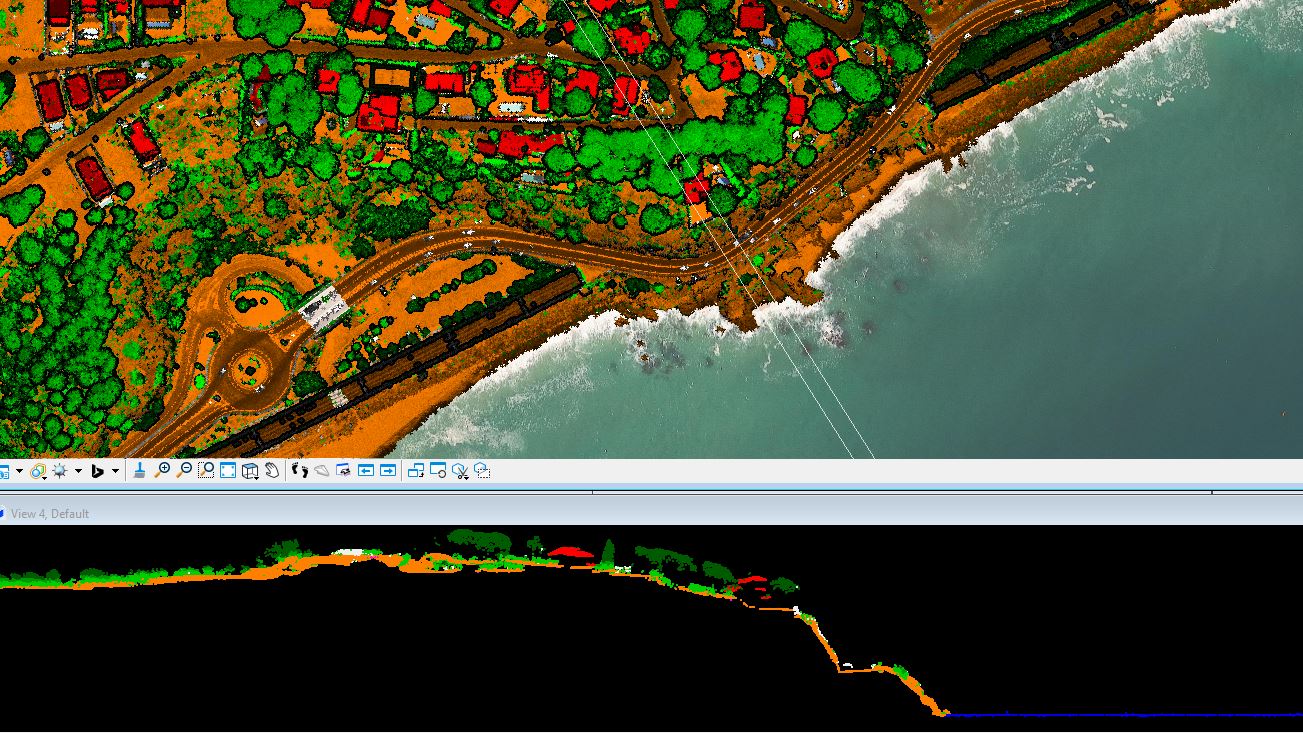
LiDAR data captured on the coastal strip allows the characterization of coastal vegetation, such as dunes with plant cover, wetlands or protected natural spaces. The classification of points makes it easier to distinguish between terrain and vegetation, which allows the calculation of heights, density and structure of the plant cover. This information is key for the management of coastal habitats, monitoring of regeneration processes and assessing the effect of storms on vegetation.

Winter coast 2024-2022 Sant Antoni de Calonge (Baix Empordà)
Volumetric studies
LiDAR point clouds are a fundamental tool for calculating volumetrics in coastal environments, such as the volume of sand on beaches, dunes or artificial breakwaters. These data allow monitoring the loss or gain of sediments after storms, planning regeneration actions and evaluating the effectiveness of coastal protection infrastructures. The precision of LiDAR-derived models ensures reliable estimation in highly dynamic areas.
Winter coast 2022 Punta Canyadell (Arenys de Mar, Maresme)