Geophysical testing of boreholes
Measurement of physical parameters along a borehole
The objective of geophysical logging of a borehole is to characterize the drilled materials (formation) and/or the fluid present in the borehole. This characterization is based on various measured physical parameters, such as the electrical resistivity of the material, the propagation velocity of seismic waves, and the temperature and conductivity of the fluid. These physical parameters are measured continuously or at specific points using different probes (sensors) that are moved along the borehole.
- Continuous logging: The variation of the physical parameters of the materials along the borehole limits the visual lithological interpretation of the core sample obtained.
- Break-through logging: Geophysical logging allows for the resolution of lithological changes in areas where samples could not be recovered.
Furthermore, the geophysical information obtained provides parameter ranges of the different materials necessary for modeling their behavior, as well as parameters that define the quality of the fluid or its transport and movement zones.

Example of geophysical evidence from a borehole with lithological interpretation based on measurements of natural gamma radiation, P-wave velocity and electrical conductivity of the formation. Temperature and fluid conductivity logs with temperature gradient are included.
Finally, geophysical evidence helps to geologically correlate nearby drillings based on the variation in their physical parameters.

Example of natural gamma radiation records in drillings in the same area. The correlation between natural gamma radiation maxima helps define reference stratigraphic levels.
The type of information that can be provided in each study depends on the conditions of the survey..
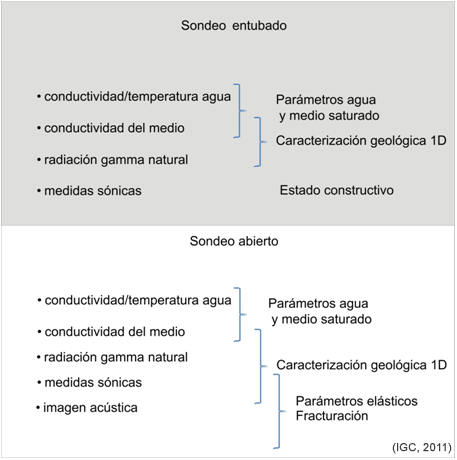
Ejemplo de la información obtenida con las sondas del IGC en función de las condiciones del sondeo.
Applications
- Detection of cavities and fractures (geological hazards, engineering).
- Detection of water levels, intrusions and contaminations (hydrogeology, environment).
- Geological studies for the determination of material parameters (strata and layers).
- S-wave velocity (seismology).
- Geothermal and geophysical parameters (engineering, geotechnics, environment).